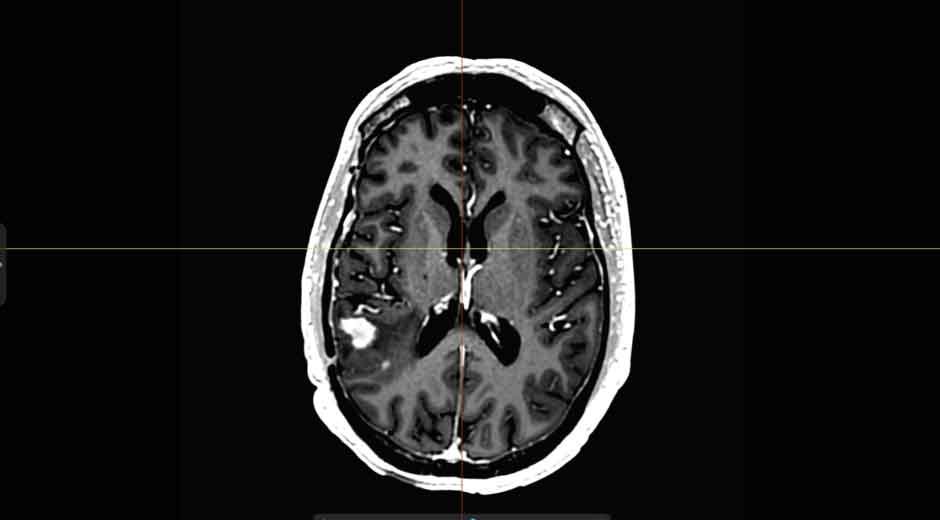
Advances in medical imaging have revolutionized the understanding and treatment of rare brain disorders. Neuroradiology, a specialized field focused on imaging the brain and central nervous system, plays a significant role in identifying these conditions. Through its tools and techniques, neuroradiology offers detailed insights that support accurate diagnosis and effective treatment strategies. Below, we explore how this field aids in understanding rare brain disorders and its broader applications.
Contents
How Are Rare Brain Disorders Defined?
Rare brain disorders encompass a diverse group of conditions affecting a small percentage of people. These disorders often have complex causes, ranging from genetic abnormalities to infections or developmental issues. A disorder is typically classified as rare when it impacts fewer than 200,000 people in the United States.
Some rare brain disorders include conditions like primary cerebral vasculitis, certain types of encephalitis, and inherited metabolic syndromes. These disorders can result in a variety of symptoms, such as seizures, cognitive decline, or uncoordinated movements. Identifying the specifics of each disorder is challenging without precise diagnostic tools, which is where neuroradiology proves valuable. Accurate diagnosis of rare brain disorders often involves collaboration across specialists and comprehensive patient assessments. Neuroradiologists, with their expertise in imaging technologies, contribute to this process by identifying structural or functional abnormalities that other testing methods might overlook.
Which Imaging Tools Do Neuroradiologists Use?
Neuroradiologists rely on a variety of imaging tools to evaluate the brain’s structure and function. Below are some commonly used methods and their roles in helping diagnose rare brain disorders:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides high-resolution images of soft tissues, allowing specialists to detect structural changes in the brain. Functional MRI extends this by revealing areas of brain activity.
- Computed Tomography (CT): Delivers detailed cross-sectional images, often used to identify conditions like brain swelling, bleeding, or abnormalities in fluid spaces.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET): Measures metabolic activity in the brain, offering data that contributes to understanding neurodegenerative diseases or tumors.
- Angiography: Visualizes blood vessels to detect abnormalities, such as aneurysms or vascular malformations. Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) further enhances image clarity.
Each modality provides a unique perspective, enabling neuroradiologists to piece together a comprehensive picture of the brain’s health. The choice of imaging technique depends on the suspected condition and its characteristics.
Can Neuroradiology Guide Treatment Planning?
The detailed imaging results produced by neuroradiology help inform treatment decisions for rare brain disorders. Imaging not only reveals the underlying condition but also provides information about its severity and progression. Effective treatment planning often relies on these insights.
Neuroimaging helps clinicians evaluate whether surgical, pharmaceutical, or other forms of intervention are likely to benefit the patient. Imaging can identify the exact location of lesions or masses, which may support surgical planning. Functional imaging might also indicate how different parts of the brain are affected, guiding therapies aimed at improving specific deficits.
Monitoring is another significant application. Repeat imaging enables medical teams to monitor the progression of a disorder over time as it responds to treatment. Adjustments to therapy may be made based on changes observed through follow-up imaging studies. Where rare brain disorders are progressive, neuroradiology findings often play a role in adapting care strategies to meet evolving patient needs.
Consult a Specialist
Diagnosing and treating rare brain disorders often involves a team of specialists, including neuroradiologists whose expertise in interpreting complex imaging plays a role. If you or someone you know is experiencing unexplained neurological symptoms, consulting a specialist is the first step. Neuroradiology imaging can offer valuable insights, aiding in early diagnosis and treatment planning. Early intervention is often key to effectively managing these conditions, so don’t hesitate to contact a healthcare provider to explore your options.